Diseases Caused By Asbestos
Asbestos exposure can cause the following health conditions:
Malignant Asbestos-Related Diseases
Malignant asbestos-related diseases are cancers caused by exposure to tiny asbestos fibers. They primarily include:
Lung Cancer
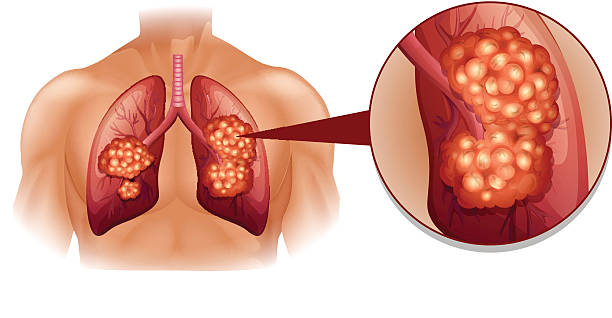
Lung cancer caused by inhaling asbestos fibers primarily affects lung tissues, particularly the cells lining the air passages.
It shares similarities with lung cancer caused by other factors but is more prevalent in individuals with a history of asbestos exposure.
Symptoms may include persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, hoarseness, unexplained weight loss, coughing up blood, and fatigue.
Mesothelioma
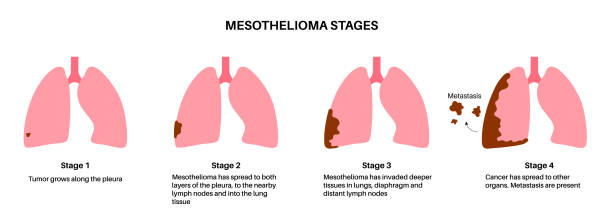
Mesothelioma is an aggressive and rare cancer that primarily affects the mesothelium, the protective lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart. It is almost exclusively caused by asbestos exposure.
Symptoms vary depending on the location of the tumor but commonly include chest pain, shortness of breath, abdominal swelling and pain, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and cough.
Laryngeal Cancer
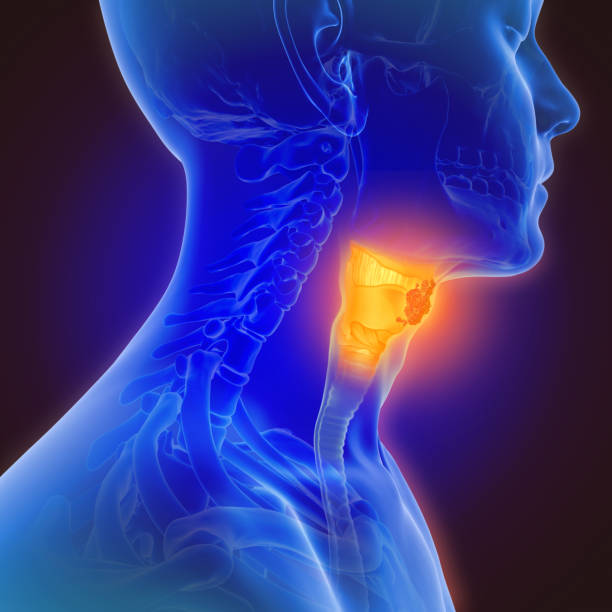
Laryngeal cancer is a malignant tumor that develops in the tissues of the larynx, or voice box.
While asbestos exposure is not the primary cause of laryngeal cancer, some studies suggest a potential association between asbestos exposure and an increased risk of laryngeal cancer.
Symptoms of laryngeal cancer may include persistent hoarseness or voice changes, difficulty swallowing, a sore throat that does not heal, a lump or swelling in the neck, persistent cough, ear pain, and breathing difficulties.
Advanced stages of laryngeal cancer may cause weight loss, fatigue, and respiratory problems.
Benign Asbestos-Related Diseases
Benign asbestos-related diseases are non-cancerous conditions caused by exposure to asbestos fibers. They primarily include:
Asbestosis
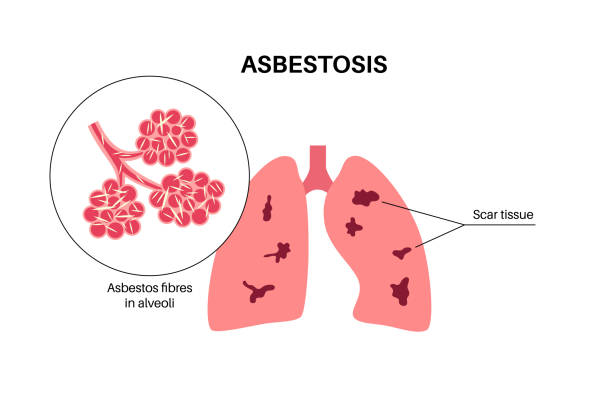
Asbestosis is a chronic lung disease caused by the inhalation of asbestos fibers. It results in scarring of lung tissue, leading to difficulty in breathing.
Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, persistent dry cough, chest tightness, and clubbing of fingers. In advanced stages, individuals may experience fatigue, chest pain, and respiratory failure.
Pleural Thickening
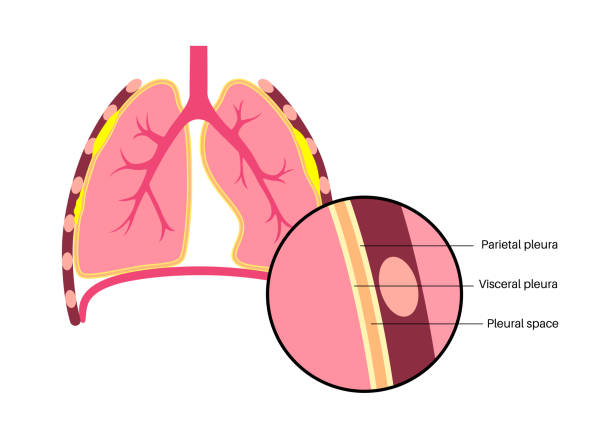
Pleural thickening is an asbestos-related disease that includes scarring and thickening of the pleura, the membrane lining the lungs and chest cavity, due to asbestos exposure. It can restrict lung expansion and cause chest pain.
Symptoms may include chest pain, chest tightness, reduced lung function, and difficulty breathing. In severe cases, it can lead to respiratory impairment.
Pleural Effusion
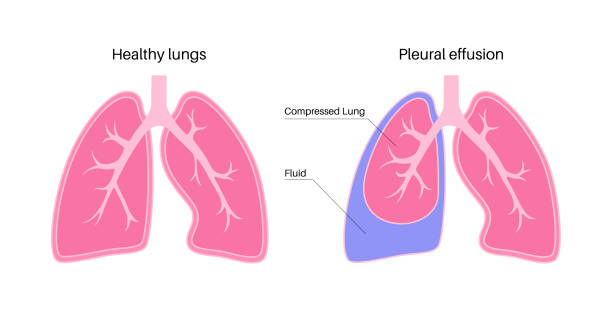
Pleural effusions are the accumulation of fluid between the layers of the pleura, often caused by inflammation or irritation from asbestos fibers. It can compress the lungs, leading to breathing difficulties.
Symptoms may include shortness of breath, chest pain, dry cough, and fever. Severe cases may cause respiratory distress and require medical intervention to drain the fluid.
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)

COPD is a chronic inflammatory lung disease characterized by airflow obstruction. While not exclusively caused by asbestos, asbestos exposure can contribute to the development or exacerbation of COPD.
Symptoms include chronic cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, chest tightness, and frequent respiratory infections.
In advanced stages, individuals may experience fatigue, weight loss, and respiratory failure.
Atelectasis
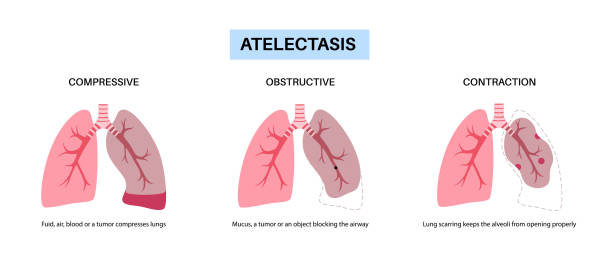
Atelectasis refers to the collapse or incomplete expansion of a lung or a portion of a lung, often due to blockage of the air passages by asbestos fibers or scarring.
Symptoms depend on the severity and location of atelectasis but may include shortness of breath, rapid breathing, chest pain, cough, and fever.
In severe cases, it can lead to respiratory distress and require medical intervention.

